Bootloader Source Code:
Phase0 Quick Start
- Make sure that your phone has had the battery and USB cable removed for at least 30 seconds.
- Connect the Neo (ie not Debug Board) to a Linux host with the USB cable.
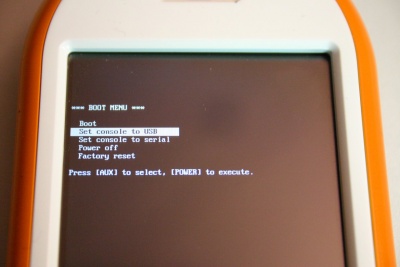
- Hold in the AUX button on power-up to access the boot menu.
- Set the console to USB.
- Connect to /dev/ttyACM0 with a terminal program on the Linux host (you might need to chown uucp.uucp /dev/ttyACM0 )
- Note that the cdc_acm /dev/ttyACM0 access disappears as soon as the Neo boots, and is replaced by the cdc_ether usb0 network access.
- You're now at the bootloader prompt.
- Set the bootdelay uboot environment variable to -1 if you want it to always halt at the bootloader on power-up.

u-boot on Neo1973 console

u-boot boot splash on Neo1973
General
The GTA01 uses the u-boot bootloader.
More information on u-boot can be found at
- http://www.denx.de/wiki/DULG
- http://www.gumstix.org/tikiwiki/tiki-index.php?page=U-Boot
- http://linuxdevices.com/articles/AT5085702347.html
Additions to the vanilla u-boot already implemented include:
- Support for boot from NAND flash using S3C2410 Steppingstone
- Support for S3C2410 NAND flash
- Support for downloading programs via S3C2410 USB Device Controller
- Support to display bootup logo / status on S3C2410 Framebuffer
However, u-boot still doesn't support many of the features that GTA01 needs, such as
- Support for reading kernel/initrd from SD/Transflash
User:HaraldWelte is working on those issues, and in fact most of them have already been implemented.
Bootloader source code
The current bootloader patches can be found at http://svn.openmoko.org/trunk/src/target/u-boot/patches/.
Untar the sources, apply the patch, run "make gta01bv3_config" (or gta01bv2_config, or whatever hardware revision you have), run "make". You will get a resulting "u-boot.bin" image, which you can directly flash (either using existing bootloader or sjf2410-linux) into NAND.
Bootloader binary
The latest bootloader binary builds can be found at http://buildhost.openmoko.org/snapshots/2007.08/images/. It should be written to the NAND flash address 0x00000000 (size 0x30000)
Bootloader development
QT2410
If you want to do bootloader development on the QT2410, it's easier to work with a bootloader image that can be downloaded via USB into RAM instead of flashing.
To do so, you need to edit the u-boot/include/configs/qt2410.h file, and change the "if 0" in Line 32 into a "if 1", then recompile with "make".
The resulting "u-boot.bin" is _NOT SUITABLE_ for NAND flash, but only for direct execution from within ram, e.g. by using the s3c2410_boot_usb program.
GTA01
Doing bootloader development on the GTA01 is a bit more tricky. first, we don't have any NOR flash. Second, there is no other way to boot _but_ from NAND. Therefore, we also don't have a USB downloader like the QT2410.
The main problem is: The S3C2410 Steppingstone unconditionally copies the first 4k of flash into its internal SRAM. That SRAM segment stays unconditionally mapped at physical address zero. How do we get around this
Using JTAG to boot from RAM
So how can we boot from RAM? We use JTAG / OpenOCD to
- Reset and halt the cpu at PC=0
> reset halt
target halted in ARM state due to debug request, current mode: Supervisor
cpsr: 0x400000d3 pc: 0x00000000
MMU: disabled, D-Cache: disabled, I-Cache: disabled
- Download a small piece of code for low-level SDRAM timing initialization (overwrite 4k SRAM of steppingstone)
> load_binary /space/misc/gta01/u-boot.git/board/gta01/lowlevel_foo.bin 0
downloaded 332 byte in 0s 21899us
- Assert a break point at address 0x33f80000 (which indicates that the low-level code has finished)
> bp 0x33f80000 4 hw
breakpoint added at address 0x33f80000
- Run the code up to the break point
> resume
Target 0 resumed
> Target 0 halted
target halted in ARM state due to breakpoint, current mode: Supervisor
cpsr: 0x600000d3 pc: 0x33f80000
MMU: disabled, D-Cache: disabled, I-Cache: enabled
- Download the u-boot RAM image to 0x33f80000
> load_binary /space/misc/gta01/u-boot.git/u-boot.bin 0x33f80000
downloaded 135692 byte in 6s 567264us
- Resume processing
> resume
Target 0 resumed
At this point, the display backlight gets bright and we see the following familiar prompt on the serial console:
U-Boot 1.1.6 (Jan 13 2007 - 23:44:23)
DRAM: 128 MB
NAND: 64 MiB
*** Warning - bad CRC or NAND, using default environment
In: serial
Out: serial
Err: serial
Hit any key to stop autoboot: 0
GTA01Bv2 #
Creating bootable images
u-boot needs bootable images (such as kernels, but also initrd and others) in form of a so-called uImage. In order to create a uImage from e.g. a vmlinux kernel image, you can proceed as follows:
objcopy -O binary -R .note -R .comment -S vmlinux linux.bin
gzip -9 linux.bin
u-boot/tools/mkimage -A arm -O linux -T kernel -C gzip -a 30008000 -e 30008000 -n "Kernel Image QT2410" -d linux.bin.gz uImage
Boot menu
As of the Phase-0 release, our u-boot version now features an on-screen boot menu.
Accessing the boot menu
You can access the boot menu by pressing and holding the Neo1973 AUX Button together with the power button while switching the phone on.
Using the boot menu
By pressing the Neo1973 AUX Button you can cycle through the menu items. Use the POWER button to select one item.
Adding items to the boot menu
You can add items to the boot menu by setting environment variables. The canonical form is menu_
For example the following command will add a boot menu entry that switches to autofast charging and turns off the backlight:
setenv menu_6 Autofast-Charge and Backlight Off: neo1973 charger autofast\; neo1973 backlight off
saveenv
While in this state, your Neo1973 can be charged with a generic USB charger. You also need to set 'setenv boot_menu_timeout 65000' to keep it from powering down, though.
Bootloader prompt
Accessing the bootloader prompt
The bootloader prompt is available either on the serial console (via Debug Board), or as virtual USB Serial device (USB CDC_ACM). Whether the serial port or usb is used depends on the u-boot environment variables stdin, stdout and stderr.
Whether or not you use usbtty, the first couple of messages will always be displayed on the serial console.
The bootloader is currently configured to wait for three seconds. If a key press on the stdin is received within those three seconds, auto-boot is aborted.
Using usbtty from Linux
Just by connecting the phone in u-boot mode to your Linux pc should make it detect a CDC ACM device, and you should get a new tty device called /dev/ttyACM0. If not, enable the CONFIG_USB_ACM (Device Drivers -> USB support -> USB Modem (CDC ACM) support). (Instructions for MacOS users are here)
Use your favourite terminal emulator (minicom, cu, zc, screen ...) to access it like any other serial port. If you don't have a favorite, try just: (cu is in the taylor-uucp package, use "apt-get install cu" if it is not yet installed)
cu -l /dev/ttyACM0
You might need to
chown uucp.uucp /dev/ttyACM0
to get the necessary right (even as root).
First, you should try to check whether the USB device shows up in 'lsusb' while you're running in u-boot mode:
# lsusb -d 1457:5119
Bus 005 Device 079: ID 1457:5119
Second, lets see some more details about the available endpoints and configurations:
# lsusb -v -d 1457:5119
Bus 005 Device 079: ID 1457:5119
Device Descriptor:
bLength 18
bDescriptorType 1
bcdUSB 1.10
bDeviceClass 2 Communications
bDeviceSubClass 0
bDeviceProtocol 0
bMaxPacketSize0 16
idVendor 0x1457
idProduct 0x5119
bcdDevice 0.00
iManufacturer 1 OpenMoko, Inc
iProduct 2 Neo1973 Bootloader U-Boot 1.2.0-g6c7cac8c-dirty-moko3
iSerial 3 0000000
bNumConfigurations 1
Configuration Descriptor:
bLength 9
bDescriptorType 2
wTotalLength 85
bNumInterfaces 3
bConfigurationValue 1
iConfiguration 4 TTY via USB
bmAttributes 0xc0
Self Powered
MaxPower 0mA
Interface Descriptor:
bLength 9
bDescriptorType 4
bInterfaceNumber 0
bAlternateSetting 0
bNumEndpoints 1
bInterfaceClass 2 Communications
bInterfaceSubClass 2 Abstract (modem)
bInterfaceProtocol 1 AT-commands (v.25ter)
iInterface 6 Control Interface
CDC Header:
bcdCDC 0.6e
CDC Call Management:
bmCapabilities 0x00
bDataInterface 1
CDC ACM:
bmCapabilities 0x00
CDC Union:
bMasterInterface 0
bSlaveInterface 1
Endpoint Descriptor:
bLength 7
bDescriptorType 5
bEndpointAddress 0x81 EP 1 IN
bmAttributes 3
Transfer Type Interrupt
Synch Type None
Usage Type Data
wMaxPacketSize 0x0010 1x 16 bytes
bInterval 255
Interface Descriptor:
bLength 9
bDescriptorType 4
bInterfaceNumber 1
bAlternateSetting 0
bNumEndpoints 2
bInterfaceClass 10 CDC Data
bInterfaceSubClass 0 Unused
bInterfaceProtocol 0
iInterface 5 Bulk Data Interface
Endpoint Descriptor:
bLength 7
bDescriptorType 5
bEndpointAddress 0x02 EP 2 OUT
bmAttributes 2
Transfer Type Bulk
Synch Type None
Usage Type Data
wMaxPacketSize 0x0010 1x 16 bytes
bInterval 255
Endpoint Descriptor:
bLength 7
bDescriptorType 5
bEndpointAddress 0x83 EP 3 IN
bmAttributes 2
Transfer Type Bulk
Synch Type None
Usage Type Data
wMaxPacketSize 0x0010 1x 16 bytes
bInterval 255
Interface Descriptor:
bLength 9
bDescriptorType 4
bInterfaceNumber 2
bAlternateSetting 0
bNumEndpoints 0
bInterfaceClass 254 Application Specific Interface
bInterfaceSubClass 1 Device Firmware Update
bInterfaceProtocol 1
iInterface 7 USB Device Firmware Upgrade
Device Status: 0x0001
Self Powered
Next, you can access it using your favourite terminal program.
Then, if the environment is not set correctly, you will need to use the current console (e.g. serial console) to set
GTA01Bv2 # setenv stderr usbtty
GTA01Bv2 # setenv stdout usbtty
GTA01Bv2 # setenv stdin usbtty
Typical u-boot prompt
U-Boot 1.2.0-moko1 (Feb 16 2007 - 00:36:13)
DRAM: 128 MB
NAND: 64 MiB
Found Environment offset in OOB..
Video: 640x480x8 31kHz 59Hz
USB: S3C2410 USB Deviced
In: serial
Out: serial
Err: serial
Hit any key to stop autoboot: 0
GTA01Bv3 #
Commands on the bootloader prompt
Auto-boot
Auto-boot executes the command[s] specified in the bootcmd environment variable. The default configuration is:
GTA01Bv3 # printenv
bootcmd=setenv bootargs ${bootargs_base} ${mtdparts}; nand read.e 0x32000000 kernel; bootm 0x32000000
This basically tells us that it will load the content of the NAND partition kernel to memory address 0x32000000 and then try to boot it.
Environment
u-boot is configured to manage a non-volatile environment that is stored in NAND flash. You can use the commands to read/alter/store the environment in the following example:
GTA01Bv2 # printenv
baudrate=115200
bootargs=rootfstype=jffs2 root=/dev/mtdblock4 console=ttySAC0,115200 console=tty0 loglevel=8 dyntick=enable lpj=252416
usbtty=cdc_acm
bootdelay=10
stdout=serial
stderr=serial
stdin=serial
mtdparts=mtdparts=neo1973-nand:0x00030000(u-boot),0x0000c000(u-boot_env),0x00200000(kernel),0x00130000(splash),0x03c94000(rootfs)
mtdids=nand0=neo1973-nand
bootargs_base=rootfstype=jffs2 root=/dev/mtdblock4 console=ttySAC0,115200 console=tty0 loglevel=8 dyntick=enable lpj=252416
bootcmd=setenv bootargs ${bootargs_base} ${mtdparts}; nand read.e 0x32000000 kernel; bootm 0x32000000
pcf50606_int1=0x40
filesize=160C000
partition=nand0,0
mtddevnum=0
mtddevname=u-boot
Environment size: 670/16380 bytes
GTA01Bv3 # setenv bootdelay 10
GTA01Bv3 # printenv bootdelay
bootdelay=10
GTA01Bv3 # saveenv
Saving Environment to NAND...
Erasing Nand...Writing to Nand... done
GTA01Bv3 #
Note: When setting multiple commands, e.g. for bootcmd, you need to escape the ';', for instance
GTA01Bv3 # setenv bootcmd mmcinit\; ext2load mmc 0 0x32000000 uImage\; bootm 0x32000000
MMC/SD
in order to initialize a MMC/SD card, you have to use the ``mmcinit command.
GTA01Bv3 # mmcinit
trying to detect SD Card...
MMC found. Card desciption is:
Manufacturer ID = 58d564
HW/FW Revision = 3 8
Product Name = 21DN!@X�
Serial Number = 445303
Month = 5
Year = 2000
READ_BL_LEN=15, C_SIZE_MULT=7, C_SIZE=3197
size = 4208984064
GTA01Bv3 #
afterwards, you can read ext2 filesystems like:
GTA01Bv3 # ext2ls mmc 01024 . 1024 .. 12288 lost+found
1544788 uImage
NAND
GTA01Bv3 # help nand
nand info - show available NAND devices
nand device [dev] - show or set current device
nand read[.jffs2] - addr off size
nand write[.jffs2] - addr off size - read/write `size' bytes starting
at offset `off' to/from memory address `addr'
nand erase [clean] [off size] - erase `size' bytes from
offset `off' (entire device if not specified)
nand bad - show bad blocks
nand dump[.oob] off - dump page
nand scrub - really clean NAND erasing bad blocks (UNSAFE)
nand markbad off - mark bad block at offset (UNSAFE)
nand biterr off - make a bit error at offset (UNSAFE)
Loading Kernel from NAND
GTA01Bv3 # nand read 0x32000000 kernel
NAND read: device 0 offset 212992, size 2097152 ... 2097152 bytes read: OK
GTA01Bv3 # bootm 0x32000000
## Booting image at 32000000 ...
Image Name: OpenMoko Kernel Image Neo1973
Created: 2007-02-15 23:54:18 UTC
Image Type: ARM Linux Kernel Image (gzip compressed)
Data Size: 1546258 Bytes = 1.5 MB
Load Address: 30008000
Entry Point: 30008000
Verifying Checksum ... OK
Uncompressing Kernel Image ... OK
Starting kernel ...
Writing new bootloader to NAND
The following set of commands loads the file u-boot.bin from ext2/mmc and flashes it into the bootloader flash partition:
GTA01Bv3 # ext2load mmc 0 0x32000000 u-boot.bin
GTA01Bv3 # nand erase u-boot
GTA01Bv3 # nand write.e 0x32000000 u-boot ${filesize}
Writing kernel to NAND
The following set of commands loads the file uImage from ext2/mmc and flashes it into the kernel flash partition:
GTA01Bv3 # ext2load mmc 0 0x32000000 uImage
GTA01Bv3 # nand erase kernel
GTA01Bv3 # nand write.e 0x32000000 kernel ${filesize}
Writing rootfs to NAND
The following set of commands loads the file rootfs.jffs2 from ext2/mmc and flashes it into the rootfs flash partition:
GTA01Bv3 # ext2load mmc 0 0x32000000 rootfs.jffs2
GTA01Bv3 # nand erase rootfs
GTA01Bv3 # nand write.e 0x32000000 rootfs ${filesize}
Please note that this will only work with root file system sizes that are smaller than the amount of memory above 0x32000000, which in the case of 64MB SDRAM is something like 32MB. Warning: you risk bricking your phone if you attempt to read in too large a file as extload appears to write the overflow into dangerous parts of memory address space.
Neo1973 related commands
Our version of u-boot supports a couple of Neo1973 specific commands:
GTA01Bv2 # help neo1973
neo1973 neo1973 info - display phone informantion
neo1973 power-off - switch off the phone
neo1973 charger status - display charger status
neo1973 charger autofast - enable automatic fast (500mA) charging
neo1973 charger !autofast - disable automatic fast (500mA) charging
neo1973 charger fast - enable fast (500mA) charging
neo1973 charger off - disable charging
neo1973 backlight (on|off) - switch backlight on or off
neo1973 vibrator (on|off) - switch vibrator on or off
neo1973 udc pullup (on|off) - switch pull-up on or off
What's the udc?
Timeouts
If the boot loader menu is on the screen, the phone will power off when there hasn't been activity for a while. This is not nice if you are working on the boot loader console, but you can make the time longer:
setenv boot_menu_timeout [seconds]
After the phone is powered on, there is a short period of time when you can connect to the console and cancel the automatic boot without going to the menu:
setenv bootdelay [seconds]
Power-off
Using
neo1973 power-off
you can switch the device off from the bootloader prompt.
Battery charger related
For a detailed description of the charger basics, see Neo1973 Battery Charger.
Inquiring the charger state
You can get the current charger status by issuing
neo1973 charger status
The following modes are possible:
- idle - no charging
- trickle - FIXME
- pre - Slow (100mA) charging, works in hardware.
- fast_cccv - Fast (500mA) charging, using Constant-Current followed by Constant Voltage (Li-Ion)
Disabling battery charging
You can disable battery charging (until the next reboot) by issuing
neo1973 charger off
Forcing fast charge
Using
neo1973 charger fast
you can force the PMU to try to do a fast (500mA) charge of the battery. It will abort if the battery is in over temperature or some other error condition occurs.
The following commands will add a boot menu entry that switches to fast charging and turns off the backlight:
setenv menu_6 Fast-Charge and Backlight Off: neo1973 charger fast\; neo1973 backlight off
saveenv
While in this state, your Neo1973 can be charged with a generic USB charger. You also need to set
setenv boot_menu_timeout 65000
saveenv
to keep it from powering down, though.
Enabling / Disabling automatic fast charge
Autofast is a feature of the PCF50606 PMU. It means that the fast_cccv mode will be automatically selected if a charger with suitable voltage is plugged in, and the battery not in over temperature condition.
| WARNING: This is potentially dangerous. Only enable autofast if you ARE SURE that you can draw 500mA from the USB connector. This is the case with a wall outlet charger, or if you are attached to a self-powered hub or a desktop PC root hub. Bus powered hubs and some laptops only provide 100mA on their USB ports and can thus not support fast charging |
You can enable or disable autofast by
neo1973 charger autofast
and
neo1973 charger !autofast
respectively.
Backlight
You can switch the backlight on and off by using
neo1973 backlight on
and
neo1973 backlight off
respectively.
Vibrator
You can switch the vibrator on and off by using
neo1973 vibrator on
and
neo1973 vibrator off
respectively.
GSM
Starting with OpenMoko patchset SVN revision 2885, u-boot contains support for powering the GSM modem, and even accessing the modem from the console.
GSM power
You can switch the GSM modem on and off by using
neo1973 gsm on
and
neo1973 gsm off
respectively.
terminal mode
You can access the GSM modem using openmoko's built-in terminal emulator in u-boot.
The following example demonstrates how:
GTA01Bv4 # neo1973 gsm on
GTA01Bv4 # terminal serial
switching s3ser0 from console into GSM mode
Entering terminal mode for port serial
Use '~.' to leave the terminal and get back to u-boot
ATE1
OK
AT+CGMI?
ERROR
AT+CGMI
FIC
OK
AT+CGMR
GTA01Bv4
OK
~[u-boot]~.
switched s3ser0 from GSM mode back into console mode
GTA01Bv4 # neo1973 gsm off
GTA01Bv4 #
| NOTE: If you're using the cu terminal emulator on your host PC to access u-boot, you have to press '~' twice in order to escape it and make sure it actually gets sent to the Neo! |
S3C2410 specific commands
GTA01Bv2 # help s3c2410
s3c2410 speed get - display current PLL speed config
s3c2410 speed list - display supporte PLL speed configs
s3c2410 speed set - set PLL speed
GTA01Bv2 # s3c2410 speed list
50 MHz
101 MHz
202 MHz
266 MHz
GTA01Bv2 # s3c2410 speed get
FCLK = 202 MHz, HCLK = 101 MHz, PCLK = 50 MHz
GTA01Bv2 # s3c2410 speed set 101
GTA01Bv2 # s3c2410 speed get
FCLK = 101 MHz, HCLK = 50 MHz, PCLK = 50 MHz
266MHz clock
You can re-configure the S3C2410 PLL to generate a 266 MHz core cpu clock (rather than the 200MHz default) by using
GTA01Bv2 # s3c2410 speed set 266
and
GTA01Bv2 # s3c2410 speed set 202
respectively.
| WARNING: The old hardware (Phase 0 - GTA01Bv3) only runs stable at 266MHz if you do not attach anything (esp. the FPC / Debug Board to the Debug Port |
TFTP on QT2410
The QT2410 cs8900a Ethernet can be used to download images via network.
First, you have to make sure that ipaddr, serverip, ethaddr' and netmaskk are set correctly in the environment:
QT2410 # printenv
ethaddr=00:01:02:03:04:05
netmask=255.255.255.0
ipaddr=192.168.100.100
serverip=192.168.100.1
TFTP kernel download
QT2410 # tftpboot 0x32000000
*** Warning: no boot file name; using 'C0A86464.img'
TFTP from server 192.168.100.1; our IP address is 192.168.100.100
Filename 'C0A86464.img'.
Load address: 0x32000000
Loading: #################################################################
#################################################################
#################################################################
#################################################################
##########################################
done
Bytes transferred = 1544788 (179254 hex)
you can then commence booting via
QT2410# bootm 0x32000000
Device Firmware Upgrade
Our version of u-boot also implements USB DFU. This can be useful to load files and kernel for quick testing.
To find out whether your version of u-boot supports this, use the output of
$ lsusb -v -d 1457:5119
while the phone is in u-boot mode.
If it supports DFU, you should see the following snippet towards the end of the output:
Interface Descriptor:
bLength 9
bDescriptorType 4
bInterfaceNumber 2
bAlternateSetting 0
bNumEndpoints 0
bInterfaceClass 254 Application Specific Interface
bInterfaceSubClass 1 Device Firmware Update
bInterfaceProtocol 1
iInterface 0
For information on how to do firmware upgrades, please see dfu-util.
Booting files over DFU
To load a file at memory address 0x32000000:
dfu-util -a 0 -D fileToLoad -R
After that, send 'bootm 0x32000000' to u-boot or 'bootelf 0x32000000' if its an elf file.
Simple python script that can boot an ELF image - avoiding a ACM bug that breaks on large packets.
#!/usr/bin/python
import sys
import os
import time
cmd1 = "neo backlight off\n"
cmd2 = "bootelf 0x32000000\n"
def output(tty, str):
for x in str:
tty.write(x)
tty.flush()
if len(sys.argv) == 2:
print "Loading %s..." % sys.argv[1]
loadfile = "dfu-util -a 0 -D %s -R" % sys.argv[1]
os.system(loadfile)
time.sleep(3)
tty = open("/dev/ttyACM0", "a")
output(tty, cmd1)
output(tty, cmd2)
tty.close()
else:
print "Usage: %s elffile" % sys.argv[0]
print ""
sys.exit(2)
Troubleshooting
USB connectivity problems
I once got errors like this (in dmesg or /var/log/messages) on the host side while connecting the neo in u-boot:
usb 2-1: device descriptor read/64, error -110
usb usb2: Controller not stopped yet!
The problem disappeared at least for me by the command below on the host side. Please note that if you have usb keyboard or mouse then the command might cause trouble.. I only have PS/2 so I couldn't test it.
rmmod uhci_hcd ; modprobe uhci_hcd

No comments:
Post a Comment